The Most Common Cause Of Salmonella Infections
Kitchens are wonderful places full of amazing flavors, wonderful smells, and opportunities for expression, but they can also comprise potential health risks and hazards. Spoiled, undercooked, and improperly prepared food can cause real damage to the people you're serving or hosting, so it pays to be well-informed about the ins and outs of salmonella infections.
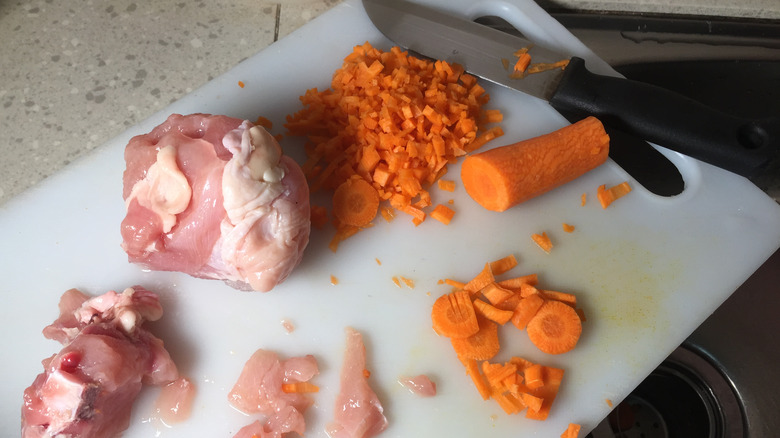
According to Mayo Clinic, salmonella infections are caused by salmonellosis, a bacteria that lives in the digestive tract of animals and humans. Generally, salmonella is contracted by consuming raw or undercooked meat, poultry, or eggs or by drinking unpasteurized milk. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention spotlights chicken, as studies and tests have shown that 1 in 25 packages of chicken found in grocery stores contain salmonella. When infected, some people don't have any symptoms at all, and others may develop stomach cramps, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, headaches, chills, and a fever, per Johns Hopkins Medicine. Oftentimes, people think they have the stomach flu when it is a salmonella infection.
The keys to health and cleanliness
Salmonella can be directly contracted by consuming raw or undercooked food, but there are other ways the bacteria can disseminate. The Mayo Clinic points to improperly handled food products and contaminated surfaces as common ways salmonella can spread to other kitchen areas. Cutting boards that have not been cleaned well after having meat on them or surfaces with meat drippings that touch other ingredients are two other examples of salmonella spreading. Make sure to keep track of your ingredients — where they are, where they're going, and be mindful of what they've been touching. And always remember to wash and disinfect used surfaces properly.
Salmonella symptoms typically last up to a week, but some people experience diarrhea for about ten days. In most cases, medical intervention is unnecessary as it goes away on its own, per Mayo Clinic. However, if the infected person is a young child, an older adult, or someone with a compromised immune system and either has been overly dehydrated or has bloody stools, contact a doctor immediately.